Breaking Down the Importance of SSL Certificates in Web Hosting
Securing your website is crucial in today’s digital world, where users increasingly demand safety to protect their sensitive information. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates have emerged as the standard for online security, playing a crucial role in ensuring the safety of data transmitted between a website and its visitors. This article breaks down the importance of SSL certificates in web hosting, exploring how they work, their benefits, and the overall significance they hold for webmasters and visitors alike.
Understanding SSL Certificates
SSL certificates in web hosting are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to a website’s data. When installed on a web server, SSL allows for secure communication between a website and users’ browsers. It encrypts the data being transmitted so that only authorized parties can decipher it, thus preventing cybercriminals from intercepting sensitive details such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal data.
How SSL Certificates Work
SSL works by using a pair of keys, a public key and a private key, to encrypt and decrypt data. When a user connects to a website with SSL enabled, their browser requests the site’s public key. The public key encrypts the data sent to the server, which can then be decrypted only using the corresponding private key.
As a result, even if an attacker intercepts the encrypted data, they cannot decipher the information without the private key. This encryption process establishes a secure channel for communication between the user and the website, protecting the data from unauthorized access.
The Importance of SSL Certificates in Web Hosting
1. Data Security
The primary aim of an SSL certificate is to secure sensitive data transmitted between users and websites. By encrypting this communication, SSL ensures that unauthorized parties cannot read or tamper with the data, ultimately safeguarding both users and website owners from cyber threats such as identity theft and data breaches.
2. Building Trust and Credibility
When a website has an SSL certificate, browsers display a padlock symbol in the address bar, and the website URL begins with “https” instead of “http”. This visual indicator helps users recognize that their data is secure, boosting trust in the website and ultimately increasing user retention, conversions, and user engagement.
3. Improved SEO Rankings
Search engines like Google understand the importance of security and have made SSL implementation a factor in their ranking algorithms. Websites that use SSL certificates are often rewarded with higher search engine rankings, ensuring greater visibility and an increased likelihood of attracting more users to the site.
4. Requirement for Online Payments
If your website processes online transactions, such as an e-commerce business or membership platform, having an SSL certificate is essential. Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance standards require SSL encryption for securing financial transactions, ultimately making an SSL certificate mandatory for websites that accept payments.
5. Protection from Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks, where cybercriminals impersonate legitimate organizations to steal sensitive information, are becoming increasingly common. SSL certificates can help protect your website and users from falling victim to these attacks by proving the authenticity of your site and reassuring visitors that they are interacting with a legitimate business.
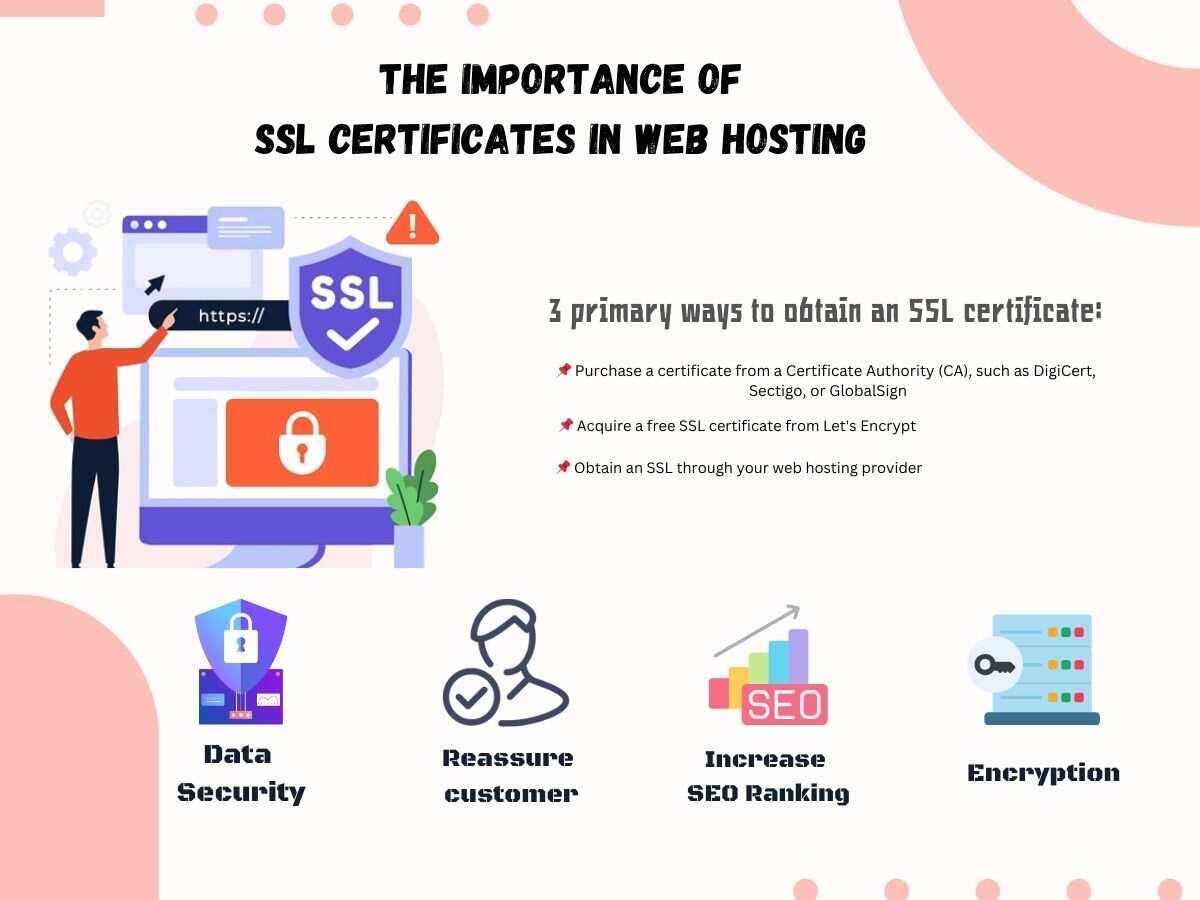
How to Get an SSL Certificates in Web Hosting
There are three primary ways to obtain an SSL certificate for your website:
1. Purchase a certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA), such as DigiCert, Sectigo, or GlobalSign. These organizations validate your domain and business, issuing an SSL certificate accordingly.
2. Acquire a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt, a non-profit CA that provides free and automated SSL certificates to website owners.
3. Obtain an SSL through your web hosting provider. Many web hosts offer SSL certificates as an add-on service, sometimes even bundling them with their hosting plans at no extra cost.